Use the filters at the top to set your initial deposit amount and your selected products. Just to clarify, in the following annuity formulas, we refer to the ordinary annuity. Now as that you know all the financial terms appearing in this calculator, let’s do a quick example of how the annuity formulas find a tax preparer can be applied. An essential aspect of distinction in this present value of annuity calculator is the timing of payments. To demonstrate how to calculate the present value of an annuity, assume that you are offered an investment that pays $2,000 a year at the end of each of the next 10 years.
Two Types of Annuities
They usually require that you make an initial lump sum payment or a series of scheduled payments, in exchange for the insurer paying to you periodic payments at a future date. To determine an individual cash flow, or annuity factor, by using this table, you would look across the top row for the number of periods and down the left side for the interest (or discount) rate. Entering these values in an equation yields the present value of an annuity.
How to calculate net present value?
As a result, this type of annuity requires that an investor spend some time managing these investments. It is important to note that variable annuities do not guarantee the return of principal. Because the funds are invested in assets that fluctuate in value, it is possible for the total value of assets in a variable annuity to be lower than the principal. Investors who cannot take on this risk are probably better off with a fixed annuity. Keep in mind that variable annuities have some of the highest fees in the financial industry.
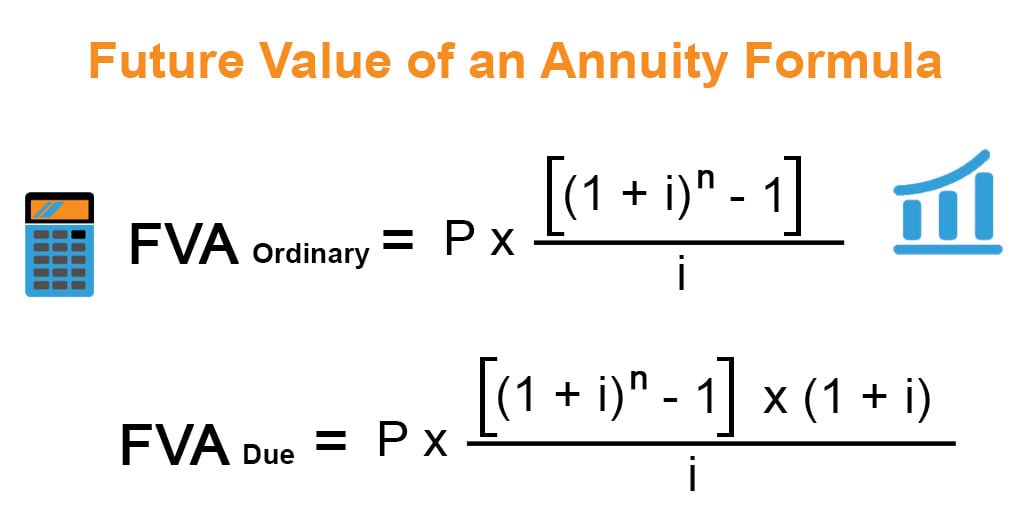
How to Calculate the Future Value of an Annuity
The crediting formulas of indexed annuities generally have some type of limiting factor that is intended to cause interest earnings to be based only on a portion of the change in whatever index it is tied to. In other words, while the index of an index annuity may have a 15% return during a year, the indexed annuity may only payout 10% of returns that year to its investor because of a cap placed on gains. Clearly, there is a tradeoff between added guarantees and receiving 100% of market gains (most variable annuities receive 100%).
Present Value Of Annuity Calculation
- It’s all simplified for you in this turn-key system that takes just 30 minutes per month.
- This type of annuity operates as a pension plan and is designed for people who are already retired and are looking for a guaranteed retirement income.
- Fortunately, our present value annuity calculator solves these problems for you by converting all the math headaches into point and click simplicity.
These annuities pay money to you after you fulfill the obligations of the contract. You may hear about a life annuity, where payments are made for the remaining lifetime of the annuitant (the person who receives the annuity payments). Since this kind of annuity is paid only under a specific condition (i.e., the annuitant is still alive), it is known as a contingent annuity. If the contract defines the period in advance, we call it a certain or guaranteed annuity.
Calculating the Present Value of an Annuity Due
The FV of money is also calculated using a discount rate, but extends into the future. Present value calculations can also be used to compare the relative value of different annuity options, such as annuities with different payment amounts or different payment schedules. The pension provider will determine the commuted value of the payment due to the beneficiary. An annuity’s future value is also affected by the concept of “time value of money.” Due to inflation, the $500 you expect to receive in 10 years will have less buying power than that same $500 would have today. Since an annuity’s present value depends on how much money you expect to receive in the future, you should keep the time value of money in mind when calculating the present value of your annuity. A number of online calculators can compute present value for your annuity.
The present value (PV) of an annuity is the current value of future payments from an annuity, given a specified rate of return or discount rate. It is calculated using a formula that takes into account the time value of money and the discount rate, which is an assumed rate of return or interest rate over the same duration as the payments. The present value of an annuity can be used to determine whether it is more beneficial to receive a lump-sum payment or an annuity spread out over a number of years. Unlike fixed annuities, variable annuities pay out a fluctuating amount based on the investment performance of assets (usually mutual funds) in an annuity. This type of annuity allows the most flexibility in terms of where investments can go, such as large-cap stocks, foreign stocks, bonds, and money market instruments.
This type of annuity operates as a pension plan and is designed for people who are already retired and are looking for a guaranteed retirement income. An indexed annuity, sometimes called an equity-indexed annuity, combines aspects of both fixed and variable annuities, though they are defined as a fixed annuity by legal statute. They pay out a guaranteed minimum such as a fixed annuity does, but a portion of it is also tied to the performance of the investments within, which is similar to a variable annuity. If an index of an indexed annuity doesn’t receive enough positive growth, the annuity investor will receive a guaranteed minimum interest return at the bare minimum.
The two most popular uses are for calculating loan payments and for calculating retirement funding needs. Both use the same formula, it’s just that they work in opposite directions. The term “annuity due” means receiving the payment at the beginning of each period (e.g. monthly rent).
Select the Show more annual cash flows checkbox of this NPV calculator to find the net present value of up to ten cash flows (investment and nine cash inflows). If you want to take into account more cash flows, we recommend you use a spreadsheet instead. However, there is a third category that is becoming increasingly common, called «indexed annuities,» which combines aspects of both. Our online tools will provide quick answers to your calculation and conversion needs.
Please enter as a percentage, but without the percent sign (for .06 or 6%, enter 6). Note that the calculator will convert the annual discount rate to the rate that corresponds to the payment frequency. For example, if you selected a monthly payment frequency, the calculator will divide the annual rate by 12. If you are trying to assess whether a particular investment will bring you profit in the long term, this NPV calculator is a tool for you. Based on your initial investment and consecutive cash flows, it will determine the net present value, and hence the profitability, of a planned project. Most insurance companies charge a surrender fee if canceled within the first 5 to 9 years of ownership.
