
Less mature companies need to retain more profit in shareholder’s equity for stability. Modern-day accounting software typically does the process of automatically debiting or crediting revenue and expense balances once the accounting period ends. An income summary is an account that is temporary and nets all the temporary accounts for a business upon closing them at the end of the given accounting period. Cash is increased with a debit, and the credit decreases accounts receivable.

How to do a balance sheet
However, note that the above calculation is indicative of the value created with respect to the use of retained earnings only, and it does not indicate the overall value created by the company. Shareholders of Apple Inc. approve the dividend declared by the board of directors amounting to 100,000. The dividend payable reduces the balance of retained earnings so it is debited in the financial books. Retained earnings, on the other hand, refer to the portion of a company’s net profit that hasn’t been paid out to its shareholders as dividends. First, revenue refers to the total amount of money generated by a company. It is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate sales and it’s reported before deducting any expenses.
- Once your cost of goods sold, expenses, and any liabilities are covered, you have to pay out cash dividends to shareholders.
- Retained earnings are a critical part of your accounting cycle that helps any small business owner grow their business.
- Once everything is in the account, businesses can easily determine if they made a profit or a loss.
- For instance, a company may declare a $1 cash dividend on all its 100,000 outstanding shares.
- After adding the current period net profit to or subtracting net loss from the beginning period retained earnings, subtract cash and stock dividends paid by the company during the year.
Accounting journal entry example
A service-based business might have a very low retention ratio because it does not have to reinvest heavily in developing new products. On the other hand, a startup tech company might have a retention ratio near 100%, as the company’s shareholders believe that reinvesting earnings can generate better returns for investors down the road. An alternative to the statement of retained earnings is the statement of stockholders’ equity. Changes in the composition of retained earnings reveal important information about a corporation to financial statement users.
- Beginning retained earnings are then included on the balance sheet for the following year.
- Retained earnings are an accumulation of a company’s net income and net losses over all the years the business has been operating.
- For instance, if a company pays one share as a dividend for each share held by the investors, the price per share will reduce to half because the number of shares will essentially double.
- This reinvestment into the company aims to achieve even more earnings in the future.
Journal Entries for Retained Earnings

It is reset to zero at the end of each accounting period and does not carry a balance forward. Net income is the first component of a retained earnings calculation on a periodic reporting basis. Net income is often called the bottom line retained earnings a debit or credit since it sits at the bottom of the income statement and provides detail on a company’s earnings after all expenses have been paid. Any net income not paid to shareholders at the end of a reporting period becomes retained earnings.
- It can have either a credit balance (indicating net income) or a debit balance (indicating net loss), depending on the period’s financial results.
- Observing it over a period of time (for example, over five years) only indicates the trend of how much money a company is adding to retained earnings.
- As a result, any factors that affect net income, causing an increase or a decrease, will also ultimately affect RE.
- For example, companies often prepare comparative income statements to analyze reports over several years.
- Shareholders, analysts and potential investors use the statement to assess a company’s profitability and dividend payout potential.
Shareholder Equity
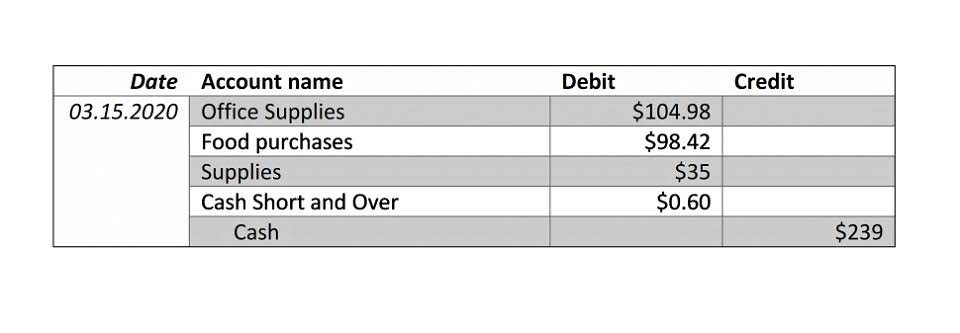
For example, if a business takes out a loan to buy new equipment, the firm would enter a debit in its equipment account because it now owns a new asset. The double-entry system provides a more comprehensive understanding of your business transactions. For example, https://www.bookstime.com/articles/solvency-vs-liquidity let’s say you need to buy a new projector for your conference room. Since money is leaving your business, you would enter a credit into your cash account. You would also enter a debit into your equipment account because you’re adding a new projector as an asset.
- Retained earnings are also the key component of shareholder’s equity that helps a company determine its book value.
- Companies that invoice their sales for payment at a later date will report this revenue as accounts receivable.
- For instance, if you prepare a yearly balance sheet, the current year’s opening balance of retained earnings would be the previous year’s closing balance of the retained earnings account.
- Retained earnings are a portion of a company’s profit that is held or retained from net income at the end of a reporting period and saved for future use as shareholder’s equity.
- In addition, debits are on the left side of a journal entry, and credits are on the right.
- In some industries, revenue is called gross sales because the gross figure is calculated before any deductions.
Negative retained earnings mean a negative balance of retained earnings as appearing on the balance sheet under stockholder’s equity. A business entity can have a negative retained earnings balance if it has been incurring net losses or distributing more dividends than what is there in the retained earnings account over the years. Instead, they reallocate a portion of the RE to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts. This allocation does not impact the overall size of the company’s balance sheet, but it does decrease the value of stocks per share.
Income statement sample

